At its core, the difference between THCA and THC is surprisingly simple: THCA is the raw, non-psychoactive compound found in fresh cannabis plants. When you apply heat, it transforms into THC, the compound famous for producing the classic “high.”
Think of THCA as the untapped potential of the plant. It’s the parent molecule, ready and waiting for heat to activate it and unlock the familiar effects of THC. This one detail is the key to choosing the right cannabis product for your goals.
Unpacking the Core Differences
On a molecular level, THCA and THC are nearly identical twins. However, even a tiny structural variation can completely change how they interact with your body, making it crucial to understand the distinction before you buy.
The secret lies in their chemical structure. THCA, or tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, has an extra piece attached called a carboxyl group. This makes the molecule too large to fit into your brain’s CB1 receptors—the gateways that trigger psychoactive effects.
But the moment you light a joint, use a vaporizer, or bake edibles, that heat triggers a process called decarboxylation. It neatly removes that extra carboxyl group, converting the non-intoxicating THCA into psychoactive THC. If you’re curious about the science, you can learn more about the chemical relationship between THCA and THC, as well as their effects.
This simple infographic sums it up perfectly—heat is the magic ingredient.
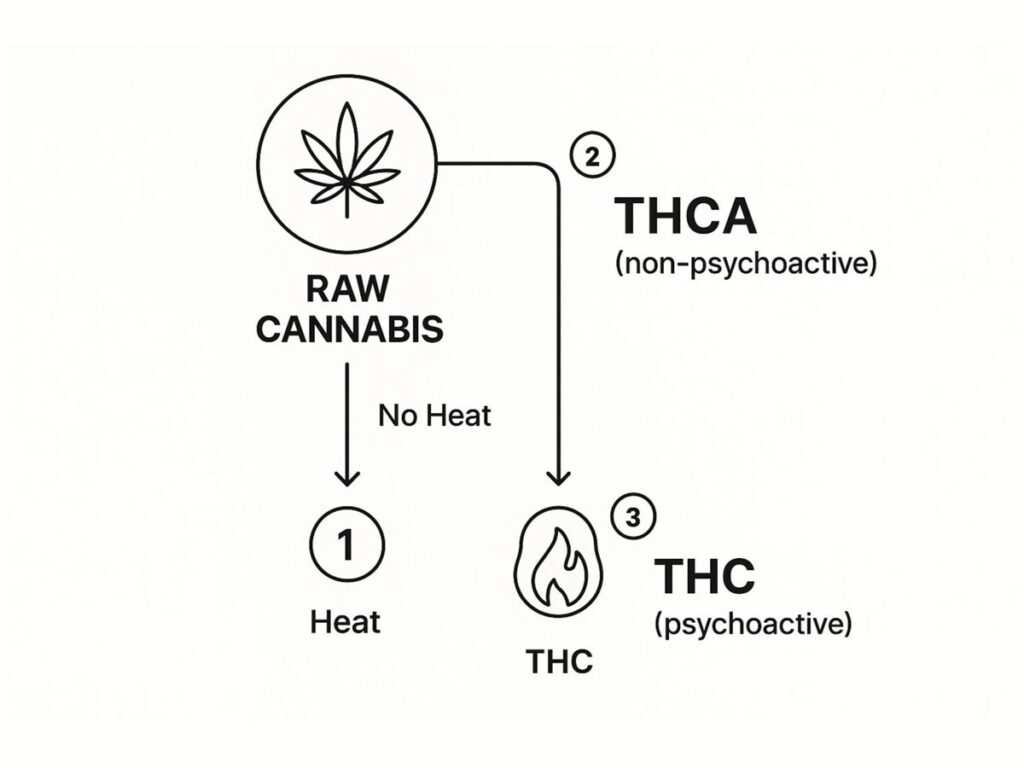
As you can see, your consumption method is everything. It’s the deciding factor in whether you experience the potential wellness benefits of THCA or the iconic effects of THC.
THCA vs THC At a Glance
So, what’s the difference between THC and THCA in a nutshell? This quick table breaks down their most important characteristics side-by-side, giving you an actionable comparison.
| Attribute | THCA (Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid) | THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol) |
|---|---|---|
| Psychoactivity | Non-psychoactive; does not produce a “high.” | Psychoactive; responsible for the euphoric “high.” |
| Source | Found in raw, unheated cannabis plants. | Created when THCA is heated (decarboxylation). |
| Primary Use Cases | Juicing raw cannabis, tinctures, topicals for potential wellness benefits without intoxication. | Smoking, vaping, edibles for psychoactive effects and therapeutic use. |
| Chemical Form | Acidic precursor with an extra carboxyl group. | Neutral cannabinoid, post-decarboxylation. |
Ultimately, understanding these distinctions empowers you to choose the right product for the experience you want, whether that’s targeted relief without the high or the well-known psychoactive effects of cannabis.
How Heat Unlocks THC’s Potential
The main barrier separating THCA from THC is a simple chemical reaction called decarboxylation. This process is the “on switch” that heat flips to convert raw, non-psychoactive cannabis into the active THC that produces a high.
Imagine the THCA molecule carrying extra baggage—a carboxyl group (COOH). This extra piece makes the molecule too bulky to connect with the brain’s CB1 receptors, which are the docking stations responsible for the “high.” When you apply heat, that baggage gets dropped.
This is exactly why chewing on a raw cannabis bud won’t get you high. You’re only consuming THCA. But the moment you smoke, vape, or cook with it, the heat initiates decarboxylation, transforming THCA into THC and allowing it to interact with your system.
The Science Behind Decarboxylation
Chemically, the process is straightforward. Heat forces the THCA molecule to release its carboxyl group, which floats away as carbon dioxide (CO2). The molecule left behind is the leaner, more effective THC, now perfectly shaped to bind with the receptors in your endocannabinoid system.
This image clearly illustrates the before-and-after at a molecular level.

As you can see, shedding that little “COOH” group makes all the difference between a non-intoxicating compound and a psychoactive one.
Of course, how you apply that heat matters. Different methods have varying levels of efficiency, which directly impacts your final experience.
- Smoking: A lighter delivers intense, immediate heat, causing rapid and near-instantaneous decarboxylation.
- Vaporizing: This method offers more control, heating cannabis just enough to convert THCA to THC without burning the plant material. You can explore the products used for this in our complete cannabis concentrates guide.
- Baking: For edibles, a “low and slow” approach is best. Heating cannabis in an oven, typically around 220-245°F, for an extended period ensures an even and thorough conversion.
Actionable Insight: It’s simple: no heat, no high. Decarboxylation is the essential step that connects the raw plant to its psychoactive effects. Your chosen consumption method determines whether this conversion happens, putting you in control.
Mastering this concept is key for anyone seeking specific results. If you’re after the classic psychoactive experience, you must use a method involving heat. If you want to tap into the potential benefits of raw cannabinoids without the high, you’ll need to avoid heat entirely.
Comparing the Effects on Your Body and Mind
Beyond the chemistry, what truly matters is how these compounds make you feel. The difference in experience between THC and THCA is like night and day, all hinging on that tiny molecular detail that dictates how each one interacts with your body. This is the core of your decision: are you seeking a psychoactive experience, or are you looking for a wellness supplement?
THC is, of course, legendary for its psychoactive effects. Once activated by heat, its specific shape fits perfectly into the CB1 receptors in your brain, like a key in a lock. This connection triggers the classic “high”—a feeling of euphoria, altered sensory perception, and deep relaxation that people use for both recreation and therapeutic relief.
Because it works so directly on these receptors, THC is a powerhouse for specific needs:
- Pain Management: It can effectively alter your brain’s perception of pain, offering a much-needed break from chronic discomfort.
- Appetite Stimulation: Known for inducing the “munchies,” it can be invaluable for anyone struggling with appetite loss.
- Nausea Reduction: THC is widely recognized for its potent anti-nausea properties, helping to settle the stomach.
That psychoactive journey is also why it’s critical to start slow, especially with edibles. If you’re new to edibles, understanding their longevity is a smart way to manage your experience and ensure it’s a positive one.
The Non-Intoxicating Power of THCA
On the other side is THCA. Its bulkier molecular structure prevents it from fitting into those CB1 receptors. The result? No high. No intoxication, no euphoria. This makes it a compelling option for people who want the potential therapeutic benefits of cannabis without any psychoactive side effects.
Instead of a mental shift, early research suggests THCA may offer other forms of support. While more studies are needed, preliminary findings point to potential anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective qualities.
Key Difference: It all comes down to the brain. THC binds strongly with the CB1 receptor, which is why it has such a profound psychoactive punch. THCA barely interacts with it, allowing it to work in the body without altering your state of mind.
Practical Scenarios: Choosing Your Path
To make this crystal clear, let’s look at two practical examples.
Scenario 1: The Wellness Seeker Imagine someone looking to manage daily inflammation without feeling high. They might add a few raw cannabis leaves to their morning smoothie. By keeping the cannabis raw and avoiding heat, they consume pure THCA, tapping into its potential anti-inflammatory properties without any psychoactive effects that could disrupt a productive workday.
Scenario 2: The Relief Patient Now, consider someone dealing with intense, chronic pain. They might choose a THC tincture or a vape for powerful, fast-acting relief. For them, the psychoactive effect is a manageable, and sometimes welcome, part of an effective pain management strategy driven by THC binding to their CB1 receptors.
In the end, the choice between THCA and THC is entirely personal. It hinges on your goals, your lifestyle, and your comfort level with psychoactive effects.
Navigating the Murky Waters of Cannabis Law
When you’re differentiating between THCA and THC, the legal landscape can be confusing. On the surface, it seems straightforward: THC is federally scheduled as a controlled substance, while THCA is often considered non-psychoactive and therefore separate.
But that’s where the simplicity ends. State and federal laws are focused on a product’s potential to get you high, not just its current state. This concept of potential conversion is where things get tricky for consumers and businesses alike.
It’s All About “Total THC”
The most important legal term to understand is “Total THC.” This isn’t just the amount of active delta-9 THC in a product. It’s a calculation that includes all the THCA that could be converted into THC with heat.
Regulators use a specific formula to prevent a loophole where high-THCA products could be sold as “low THC.” For example, a cannabis flower that tests low for delta-9 THC could still be classified as illegal marijuana if its THCA content is high enough to push its potential THC over the legal limit.
Actionable Insight: A product’s legality isn’t just about its current THC content. The law is concerned with its full psychoactive potential, which is why the THCA-to-THC conversion is a critical factor for legal compliance.
How the Farm Bill Drew the Line
The concept of “Total THC” is the foundation of modern federal cannabis law. The 2018 U.S. Farm Bill was a landmark piece of legislation that legally distinguished hemp from marijuana. The rule is clear: for a cannabis plant to be classified as legal hemp, its Total THC concentration cannot exceed 0.3% on a dry weight basis.
This 0.3% limit is based on a calculation that combines the existing delta-9 THC with the potential THC from THCA (Total THC = (THCA % * 0.877) + Delta-9 THC %). You can explore the science behind this by reviewing research on cannabinoid testing protocols.
This is precisely why you must learn to read lab reports, or Certificates of Analysis (COAs). A reputable COA provides a full cannabinoid profile, showing the exact percentages of both THCA and delta-9 THC. It’s your only tool to verify if a product is legally compliant hemp. Always remember to double-check your local and state laws, as they can be stricter than federal regulations.
Choosing The Right Consumption Method For Your Goals
Your desired outcome should be the ultimate guide when choosing between THCA and THC. The decision boils down to one practical question: to heat, or not to heat? Understanding how you consume cannabis is just as important as knowing the difference between the cannabinoids, because your method is what determines the final effect.

The rule of thumb is simple. If you apply heat, you convert THCA into psychoactive THC. If you don’t, THCA remains in its original, non-intoxicating form.
Accessing THCA Without The High
Let’s say you’re exploring the wellness potential of cannabis but have zero interest in psychoactive effects. In that case, you should stick with raw, unheated cannabis products. This approach preserves the THCA molecule, preventing its conversion into THC.
Popular and effective methods include:
- Raw Cannabis Smoothies or Juices: Blending fresh cannabis leaves or flower with your favorite fruits is a direct and simple way to consume pure THCA.
- Unheated Tinctures: Seek out tinctures specifically formulated without heat. These are designed to preserve high THCA content for easy sublingual dosing.
- Topicals and Salves: When infused into creams or balms, THCA can be applied directly to the skin for localized relief without entering the bloodstream.
Practical Insight: The raw route is ideal for anyone looking to integrate cannabis into their daily wellness routine—for its potential anti-inflammatory properties, for example—without impacting their mental clarity.
Activating THC For Psychoactive Effects
On the other hand, if you are seeking the classic high and therapeutic effects of THC, you’ll need to apply heat. This is the decarboxylation process we’ve discussed, and it’s essential for “unlocking” THC’s ability to bind with your brain’s CB1 receptors.
The most common methods for activating THC are:
- Smoking: A flame provides immediate, intense heat, which instantly converts THCA to THC for fast-acting effects.
- Vaping: Vaporizers offer precise temperature control, efficiently activating THC without combustion. For a potent and clean option, you can learn more about the best THCA hash rosin carts, which rely on this principle.
- Edibles: Baking cannabis into food involves a slower, more controlled heating process in an oven, ensuring a thorough conversion for powerful, long-lasting effects.
Choosing Your Consumption Method
This table provides a quick guide to help you match your consumption method to your desired outcome.
| Method | Primary Cannabinoid | Activation Process | Common Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Cannabis Juice | THCA | None (Consumed raw) | Wellness support without psychoactive effects |
| Smoking/Vaping | THC | Instant heat (Decarboxylation) | Fast-acting relief and psychoactive experience |
| Edibles | THC | Slow baking (Decarboxylation) | Long-lasting, potent effects for therapeutic use |
| Topicals | THCA | None (Applied to skin) | Localized relief without intoxication |
Ultimately, whether you want to enjoy the raw potential of THCA or the activated power of THC is entirely up to you. Your choice of consumption method puts you in complete control of your cannabis experience.
So, How Do You Choose Between THCA and THC?
Deciding between THCA and THC comes down to your personal goals and whether a psychoactive experience aligns with them. It’s not about which compound is “better,” but which is the right tool for your specific needs at a given moment.
Think about the end result you’re after. Are you exploring the potential wellness benefits of raw cannabis without the “high,” or are you seeking the powerful, well-known effects that only activated THC can deliver?
A Few Real-World Scenarios
Let’s walk through a couple of common situations to see where each cannabinoid shines.
- You want daily wellness support, but need to stay sharp. If you’re looking into cannabis for its potential anti-inflammatory or neuroprotective qualities and can’t have any mental fog, THCA is the clear winner. Because it’s non-psychoactive, you could add raw cannabis flower to a smoothie or use a THCA tincture without disrupting your workday.
- You need potent relief, and you need it now. For those managing significant issues like chronic pain or severe nausea, activated THC is often the more effective choice. Inhaling THC via smoking or vaping delivers it to your system rapidly, offering the immediate, powerful relief needed to manage acute symptoms.
The key is to match the cannabinoid to the situation. When you do that, you can feel confident you’re making the right choice for your lifestyle and goals.
At the end of the day, this knowledge puts you in the driver’s seat of your own wellness journey. Whether you choose the raw potential of THCA or the activated power of THC, your decision should reflect your personal health goals. As always, consulting with a healthcare professional is a smart step to ensure your choice aligns with your unique circumstances.
Common Questions About THCA and THC
Even when you understand the basics, a few questions consistently arise when people try to navigate the difference between THCA and THC. Let’s clear them up so you can move forward with confidence.
Will Consuming THCA Make Me Fail a Drug Test?
Yes, it is highly likely. Most standard drug tests are not sophisticated enough to distinguish between THCA and THC. They are designed to detect THC metabolites—the compounds your body produces after processing cannabinoids.
Furthermore, some of the THCA you consume can naturally convert to THC in your body or due to improper storage. Given the high sensitivity of modern drug tests, the safest approach is to assume that consuming any THCA product could lead to a positive test result for THC.
Can THCA Turn Into THC Without Direct Heat?
Absolutely. While a flame or vaporizer provides the fastest conversion, it’s not the only way. The process of decarboxylation can also occur slowly over time through exposure to other elements.
- Sunlight: UV rays provide enough energy to begin breaking down THCA into THC.
- Time: Over a long enough period, THCA will naturally convert to THC on its own.
- Poor Storage: Storing cannabis in a warm or brightly lit area will accelerate this process.
This is why proper storage—in a cool, dark, airtight container—is essential if your goal is to preserve the THCA in your product.
Key Insight: Think of the THCA-to-THC conversion less like an on/off switch and more like a dimmer. Heat cranks it up instantly, but factors like light and time can slowly increase the conversion, too. This highlights why product freshness and proper storage are crucial for anyone seeking a pure THCA experience.
Are There Known Side Effects of Raw THCA?
Current research is still in its early stages, but raw THCA is generally considered well-tolerated with few side effects. Because it’s non-psychoactive, you avoid the potential for anxiety or paranoia that some individuals experience with high doses of THC.
Of course, every individual’s body chemistry is unique. For trustworthy information on cannabinoid safety, you can consult reliable sources like the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. The best practice is always to start with a small amount to see how your body responds.
Ready to explore high-quality, lab-tested cannabis products for yourself? The knowledgeable budtenders at Wallflower Cannabis House are here to help you find the perfect match for your goals. Visit us today at https://wallflower-house.com/store/ to browse our selection.

