When you get right down to it, the main difference between THC and THCA is heat. It’s that simple. Imagine THCA as the raw, untapped potential in a fresh cannabis plant—it’s non-psychoactive and won’t get you “high.” THC is what THCA becomes the moment you introduce heat, unlocking the famous effects cannabis is known for.
So, when you light a joint, use a vape, or bake edibles, you’re instantly converting that dormant THCA into active THC. Understanding this simple switch is the key to choosing the right product and getting the experience you actually want.
A Direct Comparison: THCA vs. THC
Grasping the core differences between these two cannabinoids is essential for making an informed choice. While they are nearly identical on a chemical level, how they interact with your body—and the law—are worlds apart.
Think of it this way: THCA is the “potential,” and THC is the “activated” result. One exists naturally in the living plant, while the other is a creation of heat.
This transformation is a chemical process called decarboxylation. When you heat THCA, it sheds a specific part of its structure known as a carboxyl group. This tiny molecular tweak is everything—it changes the molecule’s shape just enough to let it bind perfectly with the CB1 receptors in your brain, triggering the classic psychoactive experience. Without that heat, the THCA molecule is the wrong shape and simply can’t connect with those receptors, leaving it non-intoxicating.
Key Differences at a Glance
To make it crystal clear, this table breaks down the most critical distinctions between THCA and THC.
| Attribute | THCA (Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid) | THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol) |
|---|---|---|
| Psychoactivity | Non-psychoactive; does not produce a “high.” | Psychoactive; responsible for the euphoric “high.” |
| Chemical State | The raw, acidic “precursor” found in fresh cannabis. | The activated, neutral cannabinoid created by applying heat. |
| Primary Source | Fresh, undried cannabis flower and leaves. | Smoked, vaped, or cooked cannabis products. |
| Legal Status | Often legally distinct from THC, sold under federal hemp laws. | Heavily regulated; legal for recreational use only in specific states. |
This side-by-side view powerfully illustrates how one simple action—applying heat—creates two compounds with vastly different effects and legal standings.
Here’s a visual of the THCA molecule from Wikipedia. That small extra piece on its structure is what makes all the difference.
You can see the additional carboxyl group (COOH) attached to the molecule. That’s the part heat removes to transform it into psychoactive THC.
From Plant to Potency: Unlocking the Potential
It might surprise you, but in its natural, growing state, the cannabis plant won’t get you high. It primarily produces cannabinoids in their acidic forms, and THCA can make up as much as 90% of the total THC content in a freshly harvested plant.
Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) is the direct precursor to tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). The magic happens through decarboxylation—the scientific term for what occurs when you light up, vape, or bake your cannabis. This heating process is what converts the dormant THCA into potent, active THC. For a deeper look at this chemical conversion, the National Institutes of Health offers more detailed research.
The Chemical Shift: How THCA Becomes THC
Ever wonder why you can’t just eat a raw cannabis nug and get high? The answer lies in a fascinating bit of chemistry that transforms the plant’s compounds, and it all boils down to one simple ingredient: heat.
Fresh, raw cannabis is packed with THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid), a non-psychoactive compound. It’s essentially THC in its raw state, with all its potential locked away. To unleash the effects everyone associates with cannabis, THCA must undergo a process called decarboxylation.
It sounds technical, but it’s straightforward. Applying heat removes a specific part of the THCA molecule called a carboxyl group (COOH). Once that group is gone, the molecule changes shape and becomes THC—the compound that can now perfectly interact with our body’s endocannabinoid system to produce a “high.”
This transformation is the core of the THC vs. THCA debate. Without heat, you’re left with THCA, which has its own potential benefits but won’t produce intoxicating effects.
A Closer Look at Decarboxylation in Action
Heat is the trigger that turns dormant THCA into active THC. How much heat you apply, and for how long, makes a huge difference in the final effect.
This infographic simplifies the entire process.
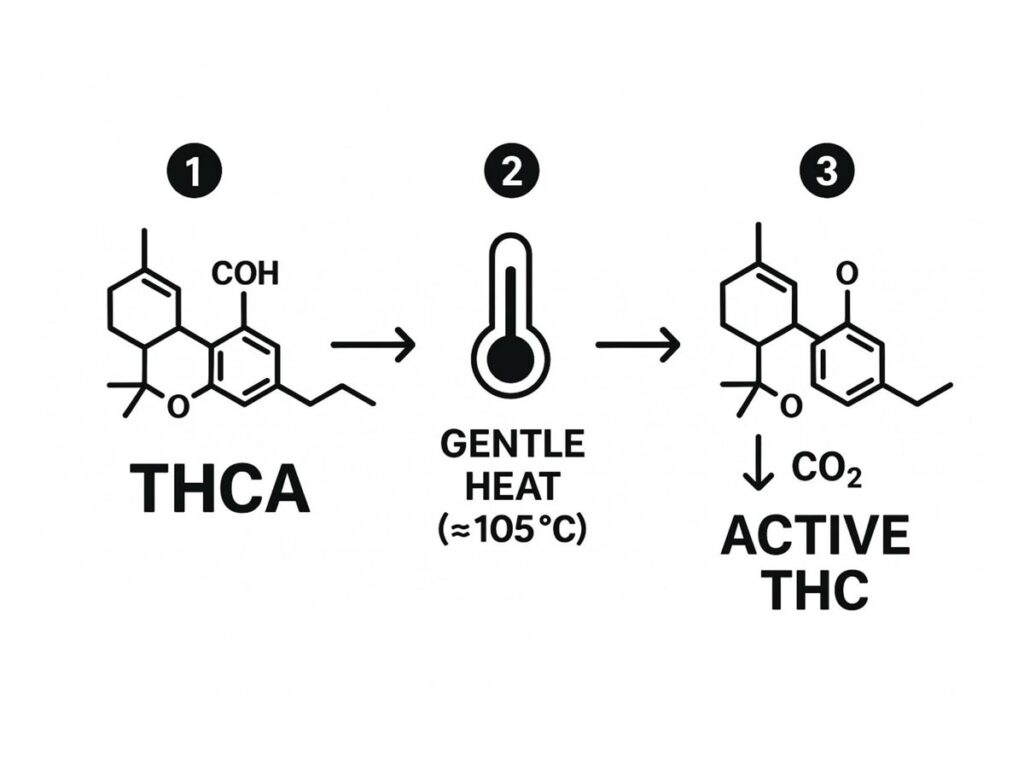
As you can see, a little heat is all it takes to alter THCA’s chemical structure, release a bit of carbon dioxide, and create the THC molecule we all know.
Here are practical examples of this science at work:
- Smoking or Vaping: This is decarboxylation on demand. The intense, immediate heat from a lighter or vape instantly converts THCA into THC right as you inhale, delivering it straight into your system for fast-acting effects.
- Baking Edibles: This method is all about “low and slow.” To make potent edibles, you first need to bake your cannabis—a common recommendation is 220-245°F (105-120°C) for 30-40 minutes. This controlled heating ensures all the THCA converts before you infuse it into butter or oil, making your edibles effective.
- Making Concentrates: Crafting products like oils, waxes, and shatters often involves decarboxylation at some stage to achieve the desired potency and consistency. To dive deeper into how different concentrates are made, check out our cannabis concentrates guide.
The Slow, Natural Conversion
While heat is the fastest method, it’s not the only one. THCA is a somewhat unstable molecule that will gradually convert to THC on its own over time, especially when exposed to oxygen and UV light.
This natural conversion starts the moment the plant is harvested. During the drying and curing process, a small amount of decarboxylation naturally occurs. This slow, patient transformation is a key reason why properly cured flower provides a smoother, more well-rounded experience compared to a fresh plant.
Actionable Insight: Your consumption method dictates your experience. The instant flash of a lighter provides immediate THC effects, while the slow, controlled heat of baking unlocks THC for edibles. Understanding this puts you in control of your cannabis journey.
How Each Compound Interacts with Your Body
The real difference between THC and THCA isn’t just a chemistry lesson—it completely changes how each one works inside you. It all boils down to their molecular shape and how they “talk” to your body’s endocannabinoid system.
Think of THC’s structure as the perfect key for a specific lock: the CB1 receptor in your brain and central nervous system. When THC binds with these receptors, it unlocks the classic psychoactive effects of cannabis—euphoria, altered perception, and relaxation. This is precisely why heating cannabis gets you “high.”
THCA, on the other hand, is shaped differently due to its extra carboxyl group. This makes the molecule too bulky to fit into the CB1 receptor. Because it can’t “turn the lock,” THCA remains non-intoxicating, allowing you to explore its potential benefits without the head-high.
The THCA Experience: Potential Without the High
Since it doesn’t cause intoxication, THCA is gaining serious attention for its unique therapeutic properties. While research is still emerging, early studies suggest it may offer benefits distinct from THC.
While THC is known for its strong connection to CB1 receptors, THCA seems to work through different pathways to influence the body, showing promise for its anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties. This makes it a compelling option for individuals seeking relief without any cognitive side effects.
Practical Example: Someone looking to manage daily inflammation might blend raw cannabis leaves (which are full of THCA) into their morning smoothie. They get the potential anti-inflammatory benefits without feeling high, so they can stay clear-headed and productive.
The THC Experience: Unlocking the Psychoactive Effects
If you’re seeking the classic cannabis experience, THC is what you need. The simple act of adding heat—from a lighter, vape, or oven—converts THCA into THC, unlocking its ability to connect with your brain’s receptors and produce that signature psychoactive journey.
The experience varies from person to person but typically includes a combination of:
- Euphoria and Relaxation: A powerful sense of calm and well-being.
- Altered Senses: Sights, sounds, and even the perception of time can feel different.
- Increased Appetite: The famous “munchies.”
- Pain Relief: Many people find it significantly eases various types of discomfort.
Your consumption method makes a huge difference. Smoking or vaping delivers near-instant effects, while edibles take longer to kick in but offer a much more prolonged experience. If you want to explore the options, our guide covers 5 ways to consume cannabis and breaks down what to expect from each.
Effects and Receptor Interaction: A Quick Comparison
This table clearly breaks down how THCA and THC interact with your body and the resulting effects.
| Factor | THCA | THC |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Receptor Interaction | Does not bind effectively with CB1 receptors. | Binds directly with CB1 receptors in the brain. |
| Psychoactive Effect | Non-intoxicating; does not produce a “high.” | Highly psychoactive; produces the classic cannabis “high.” |
| Commonly Associated Effects | Potential anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective benefits. | Euphoria, relaxation, altered perception, pain relief. |
| Primary State in Plant | Abundant in raw, unheated cannabis. | Present in very small amounts in raw cannabis. |
| Activation Method | Consumed raw (e.g., in juices, smoothies). | Activated by heat (smoking, vaping, baking). |
Ultimately, choosing between THCA and THC is about your personal goals. Are you seeking potential therapeutic benefits without the high, or are you looking for the psychoactive experience cannabis is famous for? Your answer will guide you to the right compound.
Understanding the Legal Maze: THCA vs. THC
Navigating the laws around cannabis compounds can feel overwhelming. When it comes to THCA and THC, the legal distinction hinges on one critical piece of federal legislation: the 2018 Farm Bill.
This bill legalized hemp nationwide by defining it as any cannabis plant containing less than 0.3% Delta-9 THC by dry weight. Because THCA is not Delta-9 THC in its raw state, this created a legal pathway for products high in THCA. It’s why you can often find THCA flower and vapes sold in states where traditional high-THC cannabis remains illegal.
However, it’s not that simple.
State and Local Laws: The Rules Can Change
While the Farm Bill provides a federal baseline, states have the final say. Some states have closed this “loophole” by enacting their own laws that regulate “total THC”—a value that calculates the potential THC that will be created when THCA is heated. If this total THC value exceeds 0.3%, the product is considered illegal marijuana in those states.
This means a product that is federally compliant “hemp” might be illegal where you live. These regulations are constantly evolving, so it’s crucial to understand your local laws before purchasing or possessing any THCA products.
Crucial Insight: What’s perfectly legal in one state could lead to serious trouble just across the border. Always check your local and state regulations, as they ultimately determine what is permissible in your area.
Your Best Tool for Compliance: The Certificate of Analysis (COA)
So, how can you be sure what’s in your product? Your most trustworthy resource is the Certificate of Analysis (COA). This is a lab report from an independent, third-party tester that breaks down the exact cannabinoid content.
When comparing a THC vs. THCA product, the COA provides the objective data you need. Before buying any product, you should always check the COA for two key figures:
- The Delta-9 THC level is below the 0.3% federal limit.
- The total THCA percentage matches what the product advertises.
This screenshot from the USDA website provides an overview of the official rules governing hemp production.

This official guidance highlights the federal distinction between hemp and marijuana, which is the foundation of THCA’s current legal status. For a deeper dive, you can explore the regulations directly on the U.S. Department of Agriculture website. Any reputable brand will make its COAs readily available, giving you confidence that you’re buying a product that’s both safe and compliant.
A Practical Guide to Using THCA and THC
Knowing the science is great, but putting that knowledge into practice is what really matters. Whether you’re seeking a subtle wellness boost or the classic cannabis high, your approach comes down to one simple factor: heat.
The core concept is easy: to get the benefits of raw THCA, keep it cool. To unlock the psychoactive effects of THC, apply heat. Here’s how to use both cannabinoids to achieve your desired outcome.
How to Use THCA for Non-Psychoactive Benefits
To keep THCA in its original, non-intoxicating state, you must avoid decarboxylation entirely. This means using fresh, unheated cannabis in ways that might feel new to many users.
Here are a few practical ways to incorporate raw THCA into your wellness routine:
- Add to a Smoothie: Finely grind a small amount of raw, uncured cannabis flower and blend it into your favorite smoothie. The blender does all the work, and the other ingredients will easily mask the plant’s natural flavor.
- Juice Fresh Cannabis Leaves: If you have access to fresh cannabis plants, the fan leaves are rich in THCA. Juicing them with fruits and vegetables like apples and kale is an excellent way to create a nutrient-dense, cannabinoid-rich drink.
- Use Raw Tinctures: Look for tinctures or oils specifically formulated to preserve raw cannabinoids. These are taken sublingually (a few drops under the tongue) and require no heat.
Simple THCA Smoothie Recipe: Blend a tiny pinch of raw cannabis flower (less than a gram is a good starting point) with a handful of spinach, half a banana, a cup of almond milk, and a spoonful of honey. You’ll get a nutritious boost with all the THCA and zero psychoactive effects.
How to Use THC for Its Psychoactive Effects
If you’re looking for the traditional cannabis experience, activating THC with heat is the way to go. This conversion process, decarboxylation, transforms dormant THCA into psychoactive THC. Your method will determine how quickly the effects kick in and how long they last.
Here are the most common heat-based methods:
- Smoking or Vaping: This is the most direct approach. The high temperature from a lighter or vaporizer instantly converts THCA into THC as you inhale, delivering fast-acting effects. For those who enjoy concentrates, exploring the best THCA hash rosin carts can offer a potent and flavorful experience.
- Baking Edibles: If you’re making edibles at home, you must decarb your cannabis first. Simply spread your ground flower on a baking sheet and bake it at around 220°F (105°C) for 30–40 minutes. This crucial step converts the THCA into THC before you infuse it into butter or oil, ensuring your edibles deliver the desired effect.
Common Questions About THC and THCA
Even with a solid understanding of the science, practical questions always come up when you’re deciding on a product. Let’s tackle the most common ones so you can make choices with confidence.
These are the real-world concerns, from job safety to getting the experience you actually want.
Will Consuming THCA Make Me Fail a Drug Test?
Yes, it’s highly likely. Most standard drug tests aren’t designed to tell the difference between THCA and THC. Instead, they screen for THC metabolites—the compounds your body creates after processing THC.
Since some THCA inevitably converts to THC (either slowly over time or rapidly when heated), consuming THCA products will almost certainly introduce THC metabolites into your system. If you are subject to drug testing for any reason, the safest course of action is to avoid all cannabis products, including those marketed as high-THCA hemp. It’s simply not worth the risk.
Does THCA Turn into THC on Its Own?
Absolutely. THCA is an unstable compound that is always in a slow process of converting to THC. This process is accelerated by three main factors:
- Light: UV exposure is a major catalyst.
- Air: Oxygen breaks down THCA through oxidation.
- Heat: Even room temperature will cause gradual conversion over time.
This is why that old stash you found might feel different from when you first bought it. To preserve the THCA content in your raw cannabis products, store them in a cool, dark, airtight container. But remember, a small amount of conversion is always happening.
Which One Is Better for Me: THC or THCA?
This is the ultimate question, but the answer isn’t about which compound is “better” overall. It’s about which one is better for you and your goals. The right choice comes down to one simple question.
Your desired outcome is the only thing that matters. Neither compound is superior; they just do different jobs. One offers potential wellness benefits without the high, while the other is the key to the classic cannabis experience.
To cut through the confusion, just ask yourself: “Am I looking to get high?”
- If the answer is YES, you want THC. This means you need to apply heat by smoking, vaping, or cooking. Alternatively, you can buy edibles or other products where the conversion has already been done for you.
- If the answer is NO, you’ll want to stick with THCA in its raw form. Think about adding raw cannabis to juices and smoothies or using unheated tinctures to explore its potential without the psychoactive effects.
Ready to explore the right products for your goals? The expert budtenders at Wallflower Cannabis House are here to guide you. Whether you’re looking for potent THC options or want to learn more about raw cannabinoids, our curated selection has something for everyone. Stop by the shop or check out our menu online.

